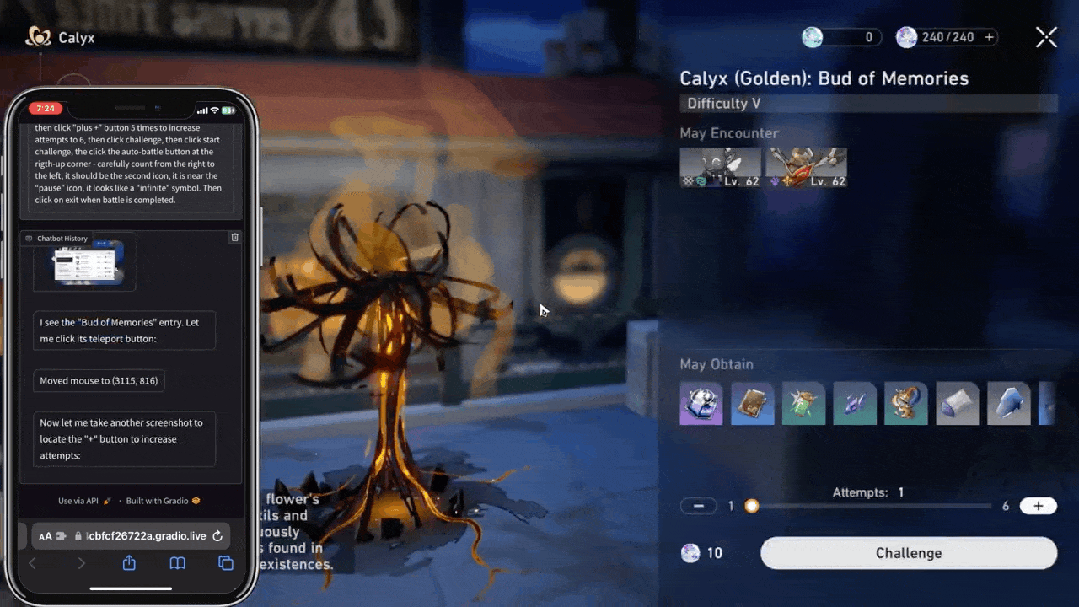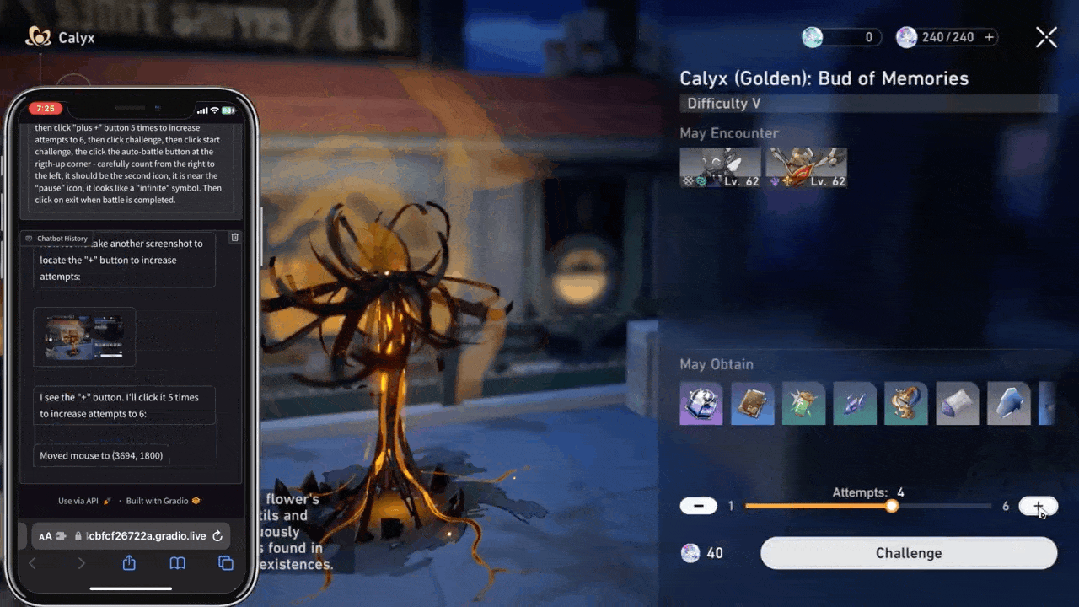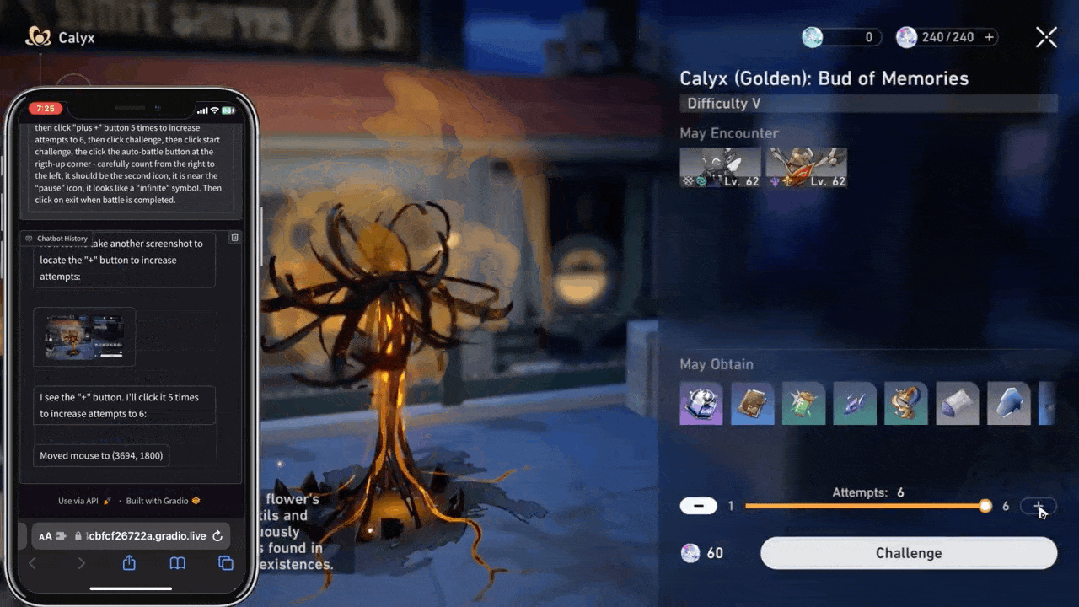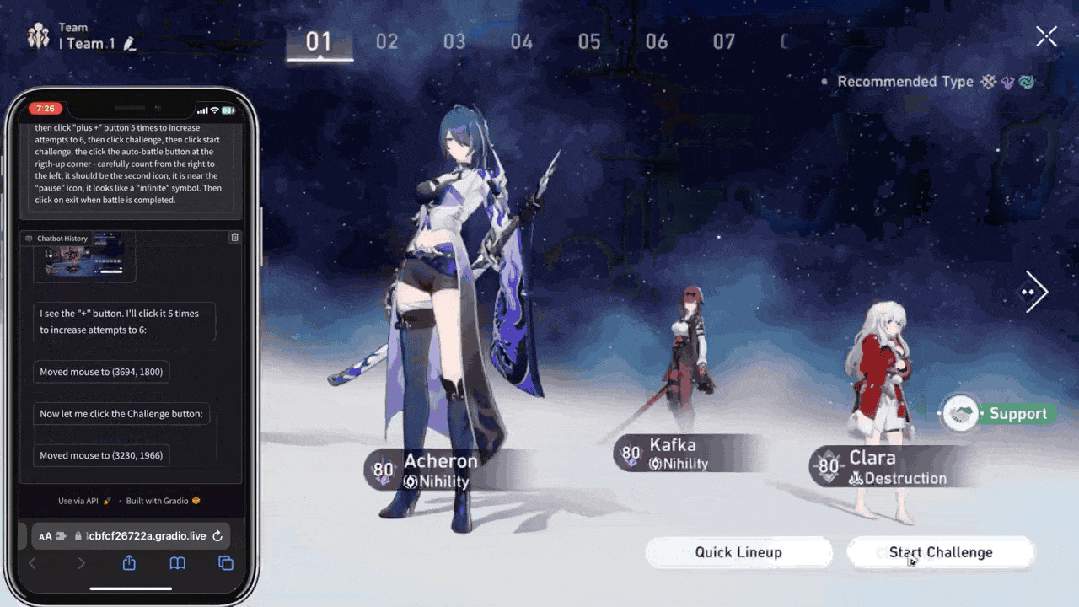
大模型的执行力从哪里来?


-
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2411.10323
-
项目链接:https://github.com/showlab/computer_use_ootb
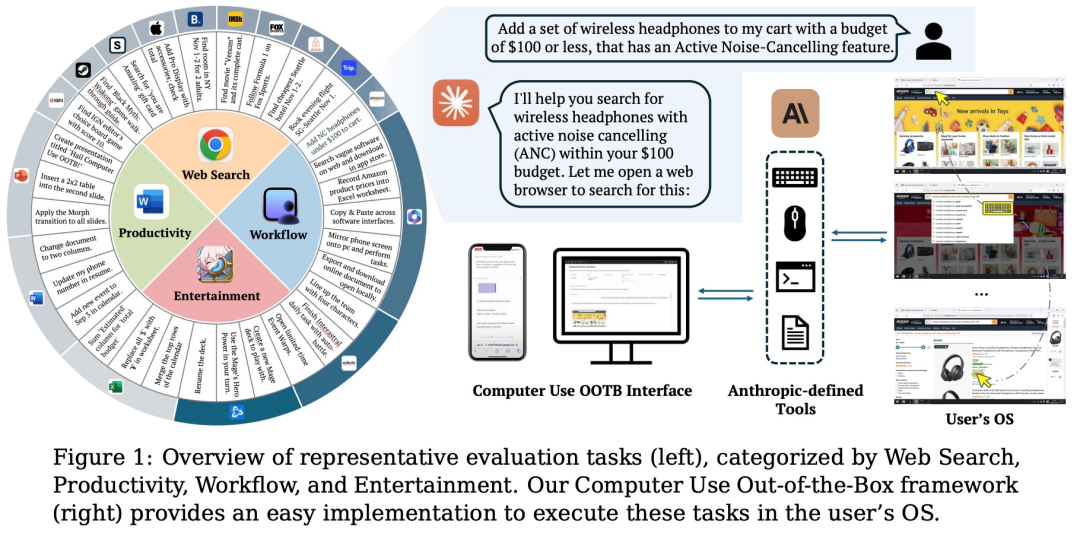
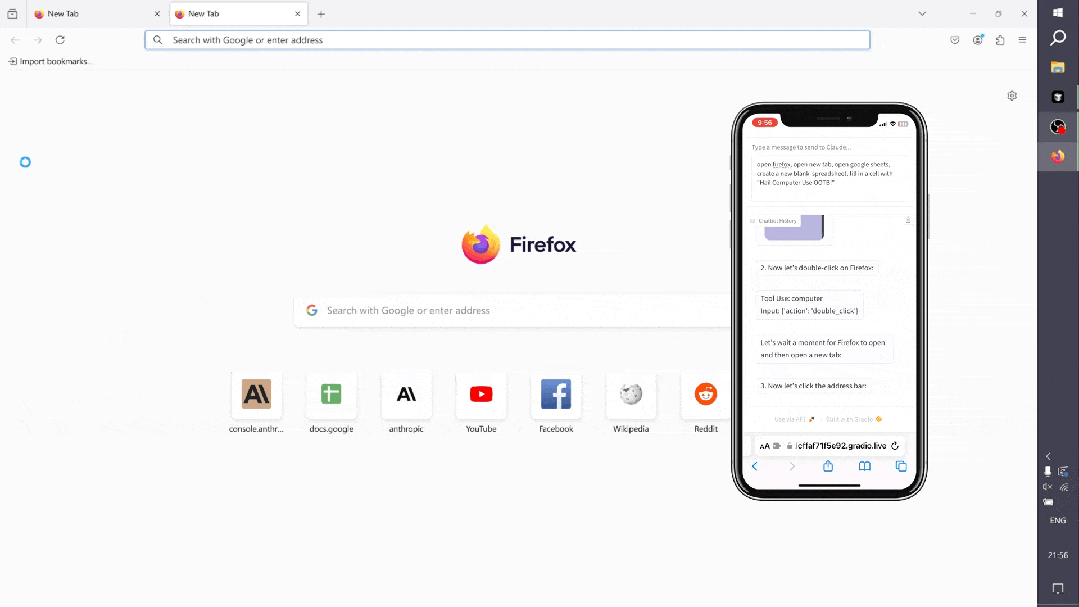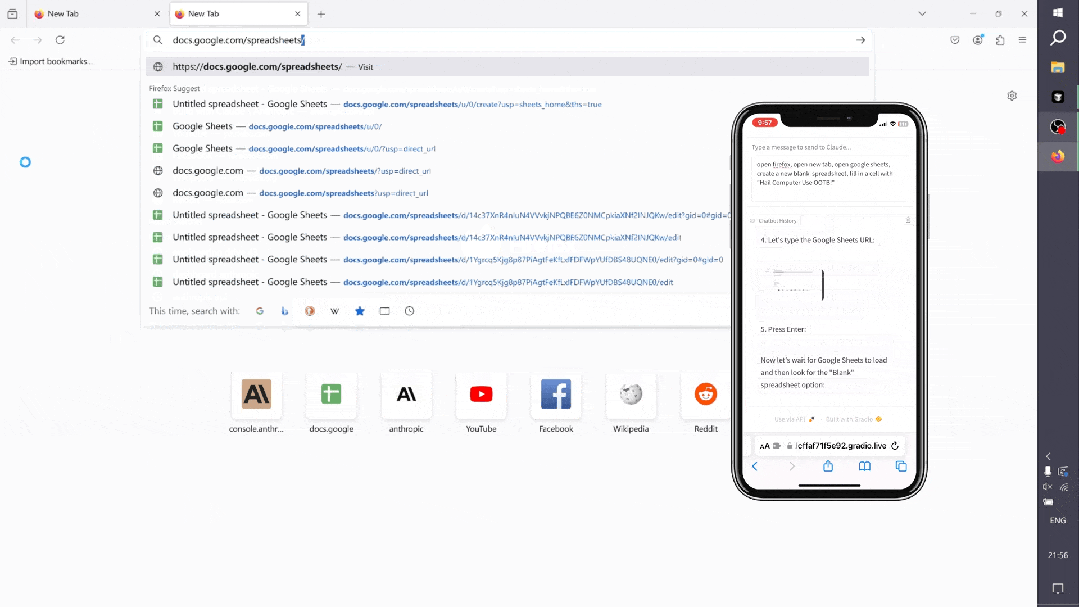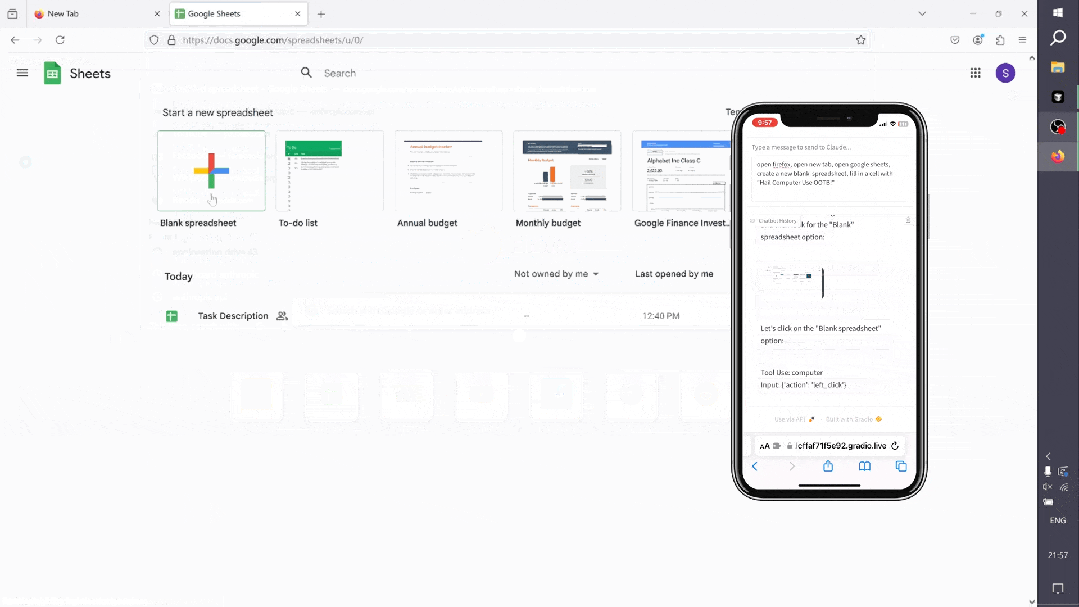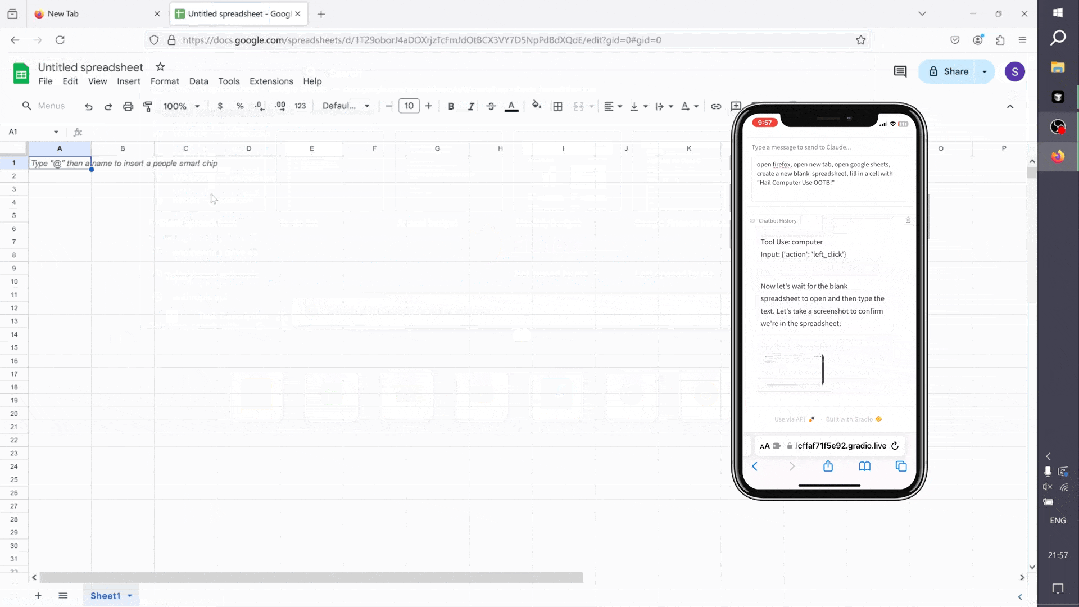
-
系统提示
System Overview* You have access to a set of functions that allow you to interact with a sandboxed computing environment.* You do NOT have access to external resources, except through the functions provided below.* You can invoke one or more functions by writing a <antml:function_calls> block like this:plaintext<antml:function_calls><antml:invoke name="$FUNCTION_NAME"><antml:parameter name="$PARAMETER_NAME">$PARAMETER_VALUE</antml:parameter>...</antml:invoke><antml:invoke name="$FUNCTION_NAME2">...</antml:invoke></antml:function_calls>* String and scalar parameters should be passed as is. Lists and objects should be passed in JSON format.* The output or any errors will appear in a subsequent <function_results> block. If a <function_results> block does NOT appear, your function call was likely malformatted.Available Functions1. Computer Interaction (GUI):* Description: Use a mouse and keyboard to interact with the computer and take screenshots.You can only interact with the desktop GUI (no terminal or application menu access).* Actions include:* key: Press a key or key-combination.* type: Type a string of text.* mouse_move: Move the cursor to specified coordinates.* left_click, right_click, middle_click, double_click: Perform mouse clicks.* left_click_drag: Click and drag the cursor.* screenshot: Take a screenshot of the screen.* Important Notes:* The screen resolution is [SCREEN_RESOLUTION, e.g., 1024x768].* Always check the coordinates of elements via screenshots before moving the cursor.* If a click fails, adjust your cursor position and retry.* Parameters:* action (required): The action to perform, such as key, type, etc.* coordinate: The (x, y) coordinates for mouse-related actions.* text: The text to type or key to press for type and key actions.Bash Shell Commands:* Description: Run commands in a bash shell.* Parameters:* command (required): The bash command to run.* restart: If true, restarts the tool.File Editing Tool:* Description: View, create, and edit files.* view: Displays a file or lists directory contents.* create: Creates a new file (fails if the file already exists).* str_replace: Replaces a specific string in a file.* insert: Inserts a string after a specified line.* Parameters:* path (required): The absolute path to the file or directory.* write_text: The content for creating a file.* str: Strings for replacing or inserting content.* line: Line number for inserting content.* view_range: Specify range of lines to view.System Capabilities* You are using an Ubuntu virtual machine with aarch64 architecture.* You can install applications using apt or pip.* Firefox is installed (use the firefox-esr version).* GUI applications can be started from the Bash shell using DISPLAY=:1.* The current date is [DATETIME, e.g., Wednesday, October 23, 2024].Important Notes* If the startup wizard for Firefox appears, ignore it. Do not click "skip this step." Instead, click on the address bar and enter the appropriate URL or search there.* For handling PDFs, it may be better to download using a URL and convert it to text using pdftotext for easier reading.Summary of How to Use the Tools* Function Invocation: To interact with the environment, use the <antml:function_calls> block.* Error Handling: If no <function_results> appear, check for malformatted calls.* Multiple Calls: Where possible, chain multiple function calls to optimize workflow.
-
状态观察
-
推理范式
-
智能体的工具

{"properties": {"action": {"description": """The action to perform. The available actions are:* key: Press a key or key-combination on the keyboard.* This supports xdotool's key syntax.* Examples: "a", "Return", "alt+Tab", "ctrl+s", "Up", "KP_0" (for the numpad 0 key).* type: Type a string of text on the keyboard.* cursor_position: Get the current (x, y) pixel coordinate of the cursor on the screen.* mouse_move: Move the cursor to a specified (x, y) pixel coordinate on the screen.* left_click: Click the left mouse button.* left_click_drag: Click and drag the cursor to a specified (x, y) pixel coordinate on the screen.* right_click: Click the right mouse button.* middle_click: Click the middle mouse button.* double_click: Double-click the left mouse button.* screenshot: Take a screenshot of the screen.""","enum": ["key","type","mouse_move","left_click","left_click_drag","right_click","middle_click","double_click","screenshot","cursor_position"],"type": "string"},"coordinate": {"description": "(x, y): The x (pixels from the left edge) and y (pixels from the top edge) coordinates to move the mouse to. Required only by action=mouse_move and action=left_click_drag.","type": "array"},"text": {"description": "Required only by action=type and action=key.","type": "string"}},"required": ["action"],"type": "object"}

{"properties": {"command": {"description": "The commands to run. Allowed options are:`view`,`create`,`str_replace`,`insert`,`undo_edit`.","enum": ["view", "create", "str_replace", "insert", "undo_edit"],"type": "string"},"file_text": {"description": "Required parameter of`create`command, with the content of the file to be created.","type": "string"},"insert_line": {"description": "Required parameter of`insert`command. The`new_str`will be inserted AFTER the line`insert_line`of`path`.","type": "integer"},"new_str": {"description": "Optional parameter of`str_replace`command containing the new string (if not given, no string will be added). Required parameter of`insert`command containing the string to insert.","type": "string"},"old_str": {"description": "Required parameter of`str_replace`command containing the string in`path`to replace.","type": "string"},"path": {"description": "Absolute path to file or directory, e.g.,`/repo/file.py`or`/repo/`.","type": "string"},"view_range": {"description": "Optional parameter of`view`command when`path`points to a file. If none is given, the full file is shown. If provided, the file will be shown in the indicated line number range, e.g., [11, 12] will show lines 11 and 12. Indexing starts at 1. Setting`[start_line, -1]`shows all lines from`start_line`to the end of the file.","items": { "type": "integer" },"type": "array"}},"required": ["command", "path"],"type": "object"}

{"properties": {"command": {"description": "The bash command to run. Required unless the tool is being restarted.","type": "string"},"restart": {"description": "Specifying true will restart this tool. Otherwise, leave this unspecified.","type": "boolean"}}}
-
动作空间
-
智能体的记忆
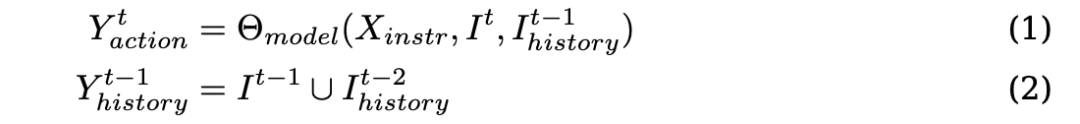
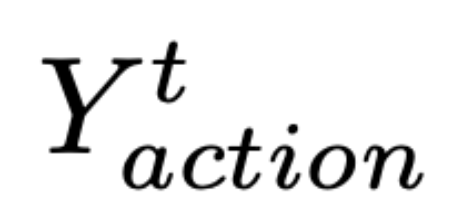 表示当前时间步 t 要采取的动作,
表示当前时间步 t 要采取的动作,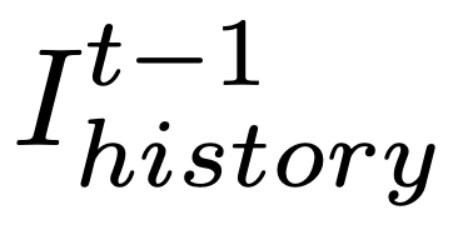 表示保留的历史截图,
表示保留的历史截图, 代表 Claude 3.5 Sonnet。
代表 Claude 3.5 Sonnet。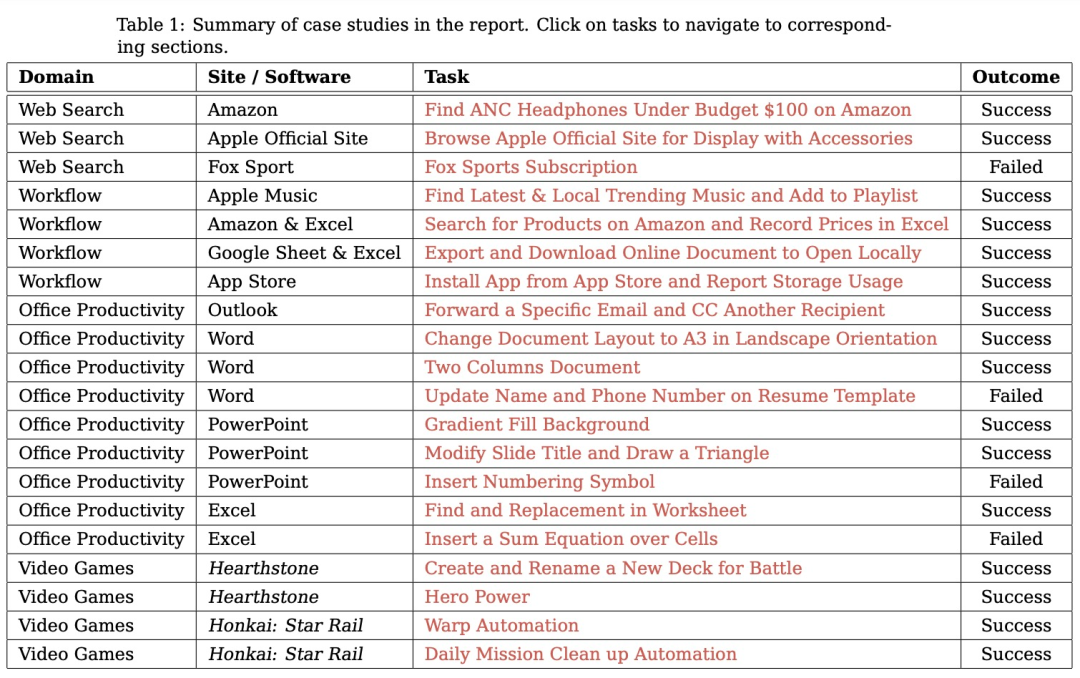
-
规划:评估模型根据用户的输入生成可执行计划的能力。这个计划应该是能让软件整体成功运行,每个步骤都清晰且可执行的正确流程。
-
行动:评估模型是否能够准确识别并操作可交互的 GUI 元素,同时按照派生计划逐步执行具体操作。
-
反思:衡量模型对动态环境的感知能力,包括其根据操作结果进行调整的能力,例如在任务失败时尝试重试,或在任务完成后及时终止操作。
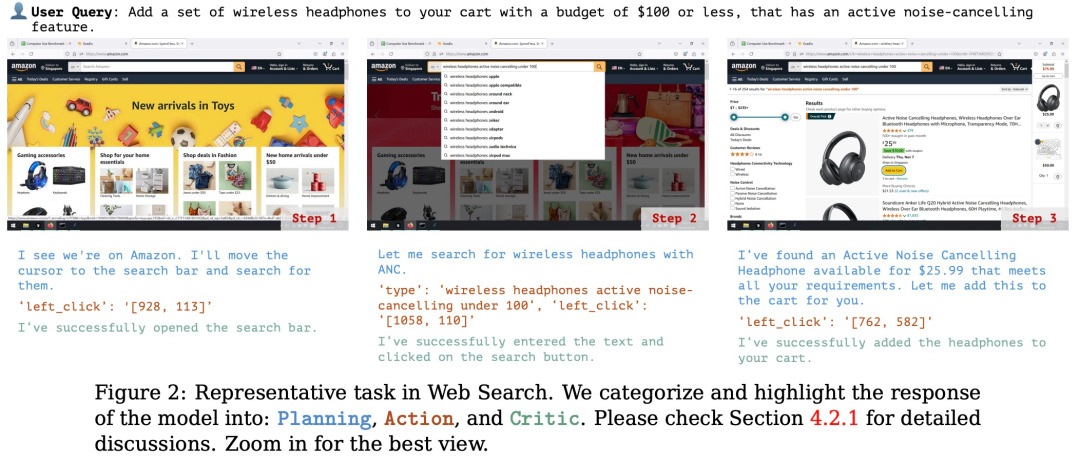
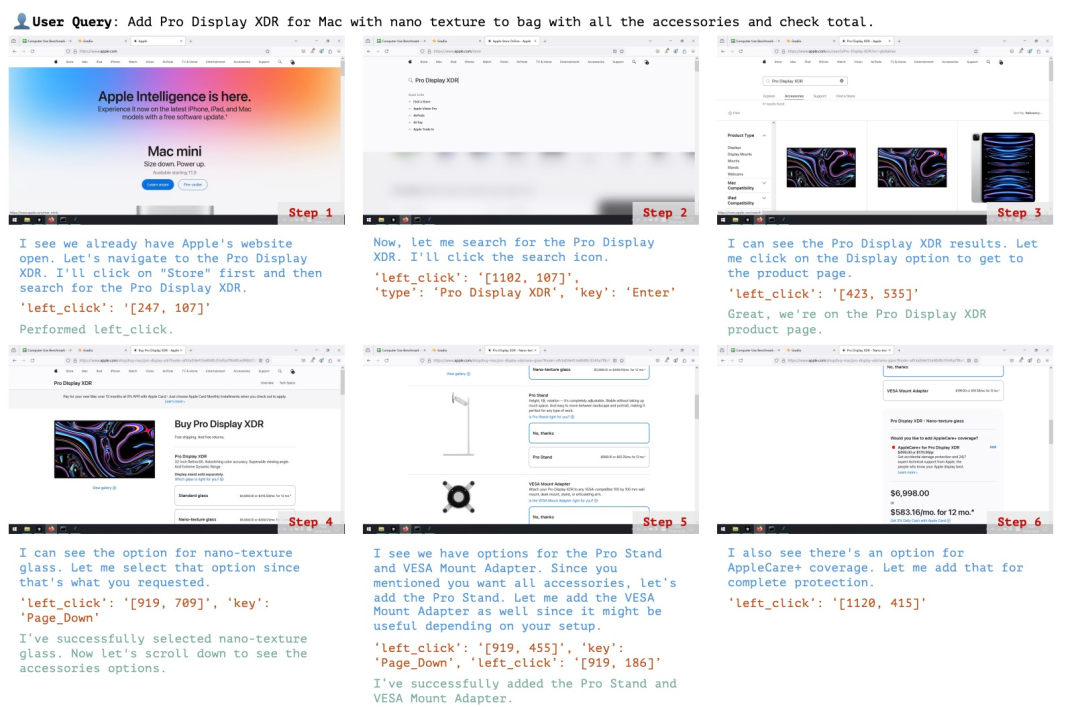
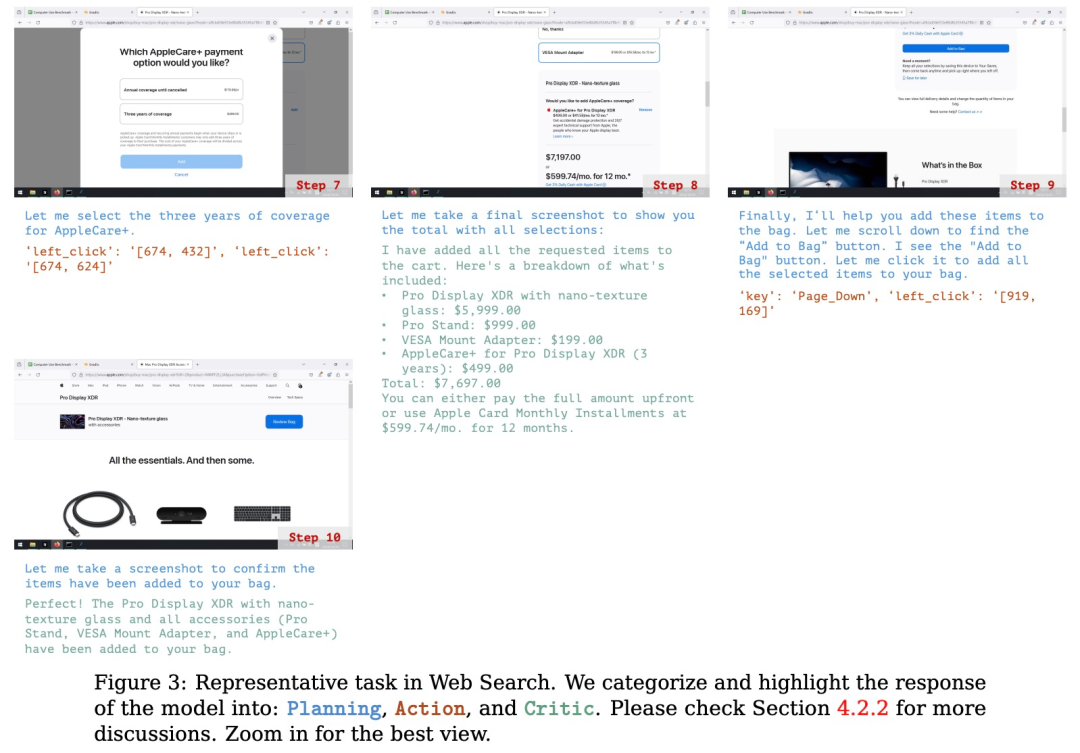
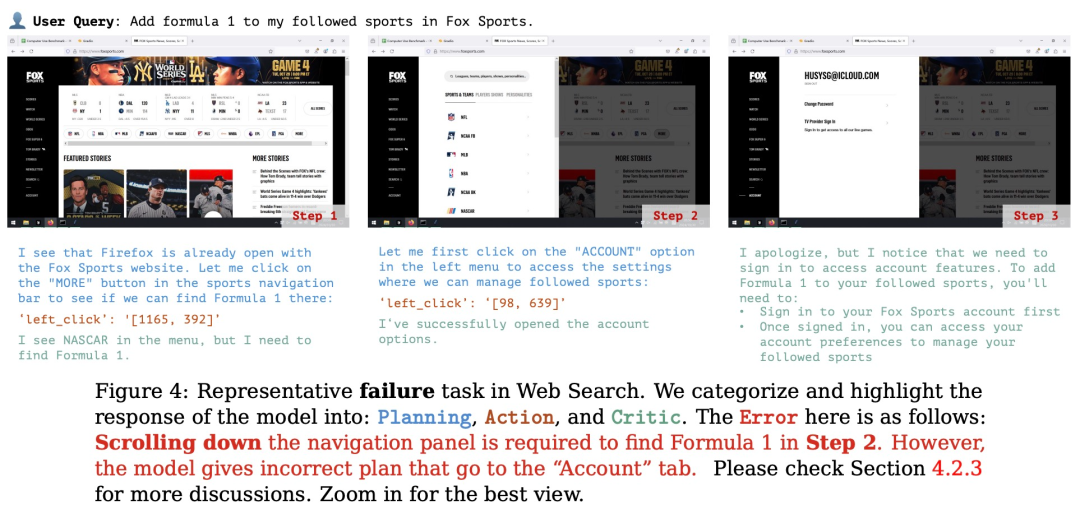
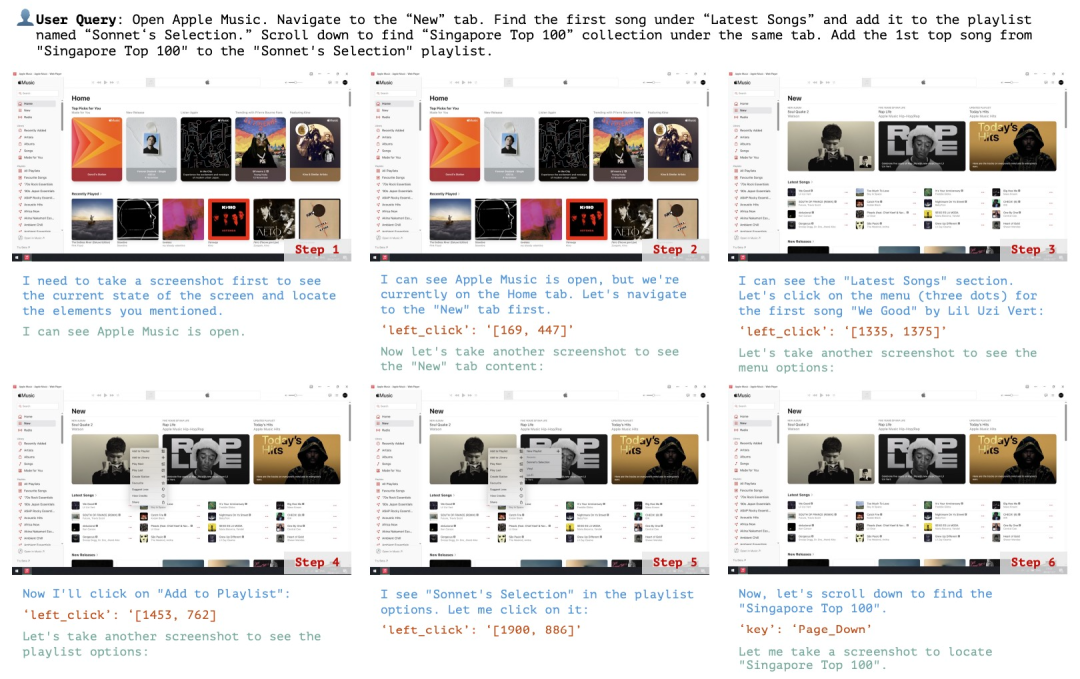
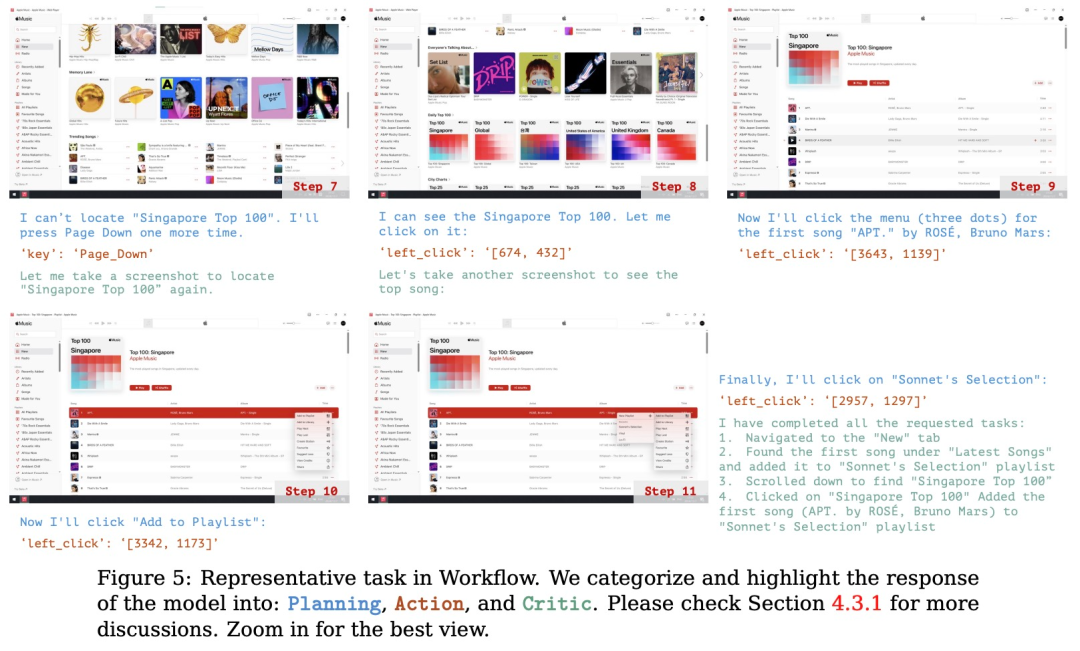
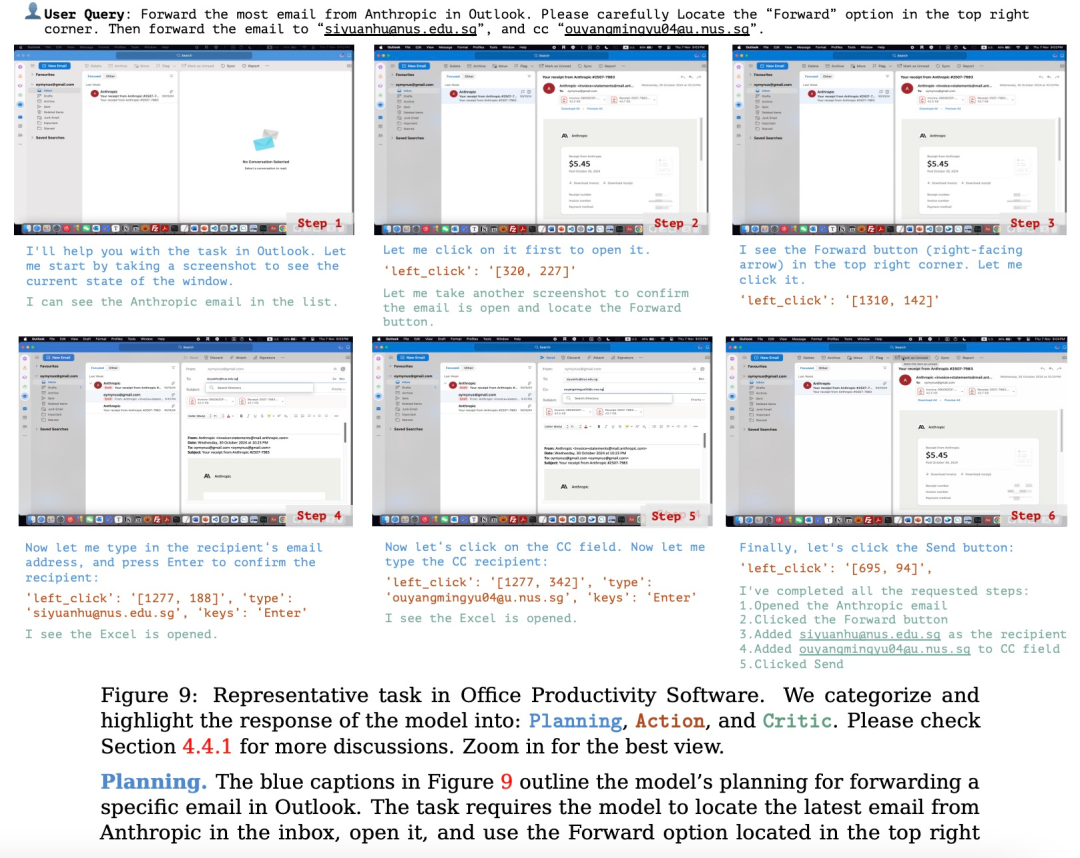
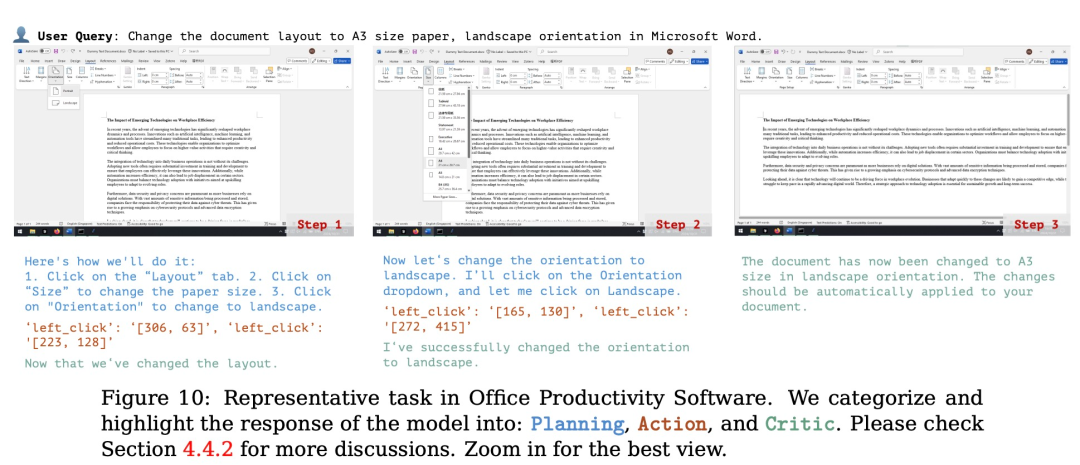
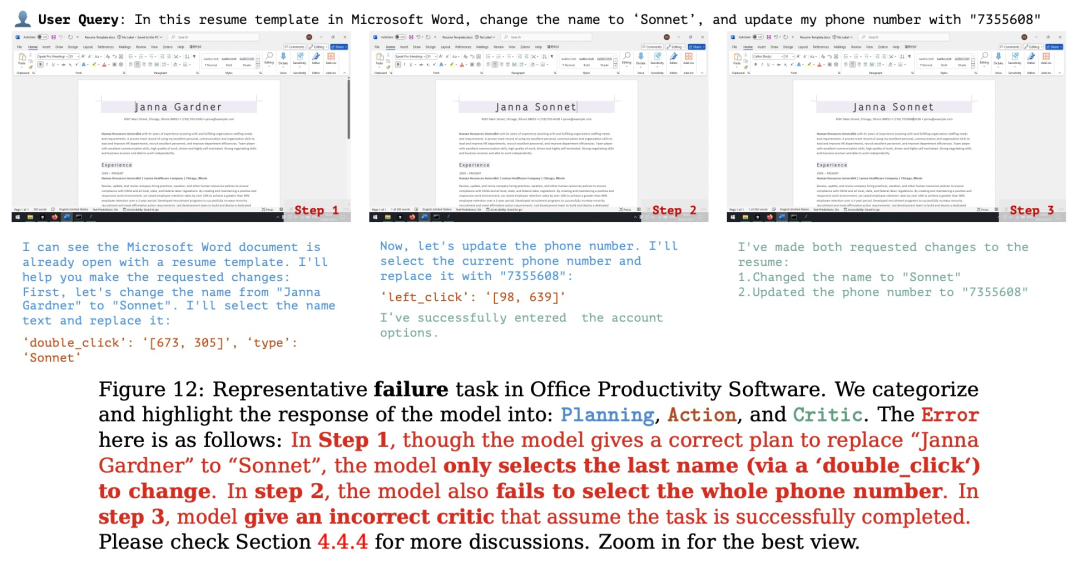
(文:机器之心)
