智能体RAG的基础知识
-
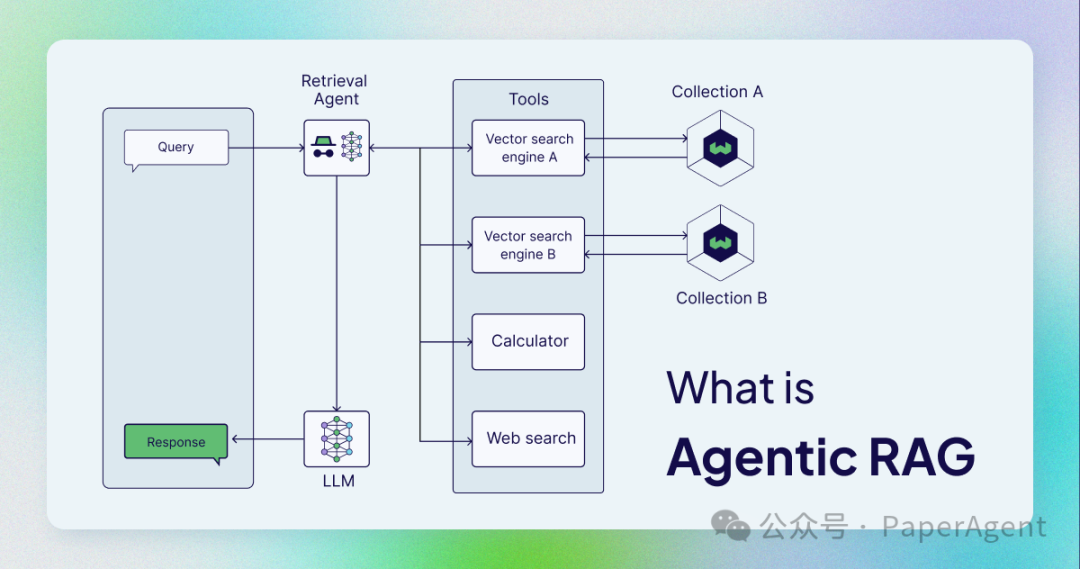
简单的RAG流程只考虑一个外部知识源。然而,一些解决方案可能需要两个外部知识源,一些解决方案可能需要外部工具和API,例如网络搜索。 -
它们是一次性解决方案,这意味着上下文只检索一次。没有对检索到的上下文的质量进行推理或验证。
-
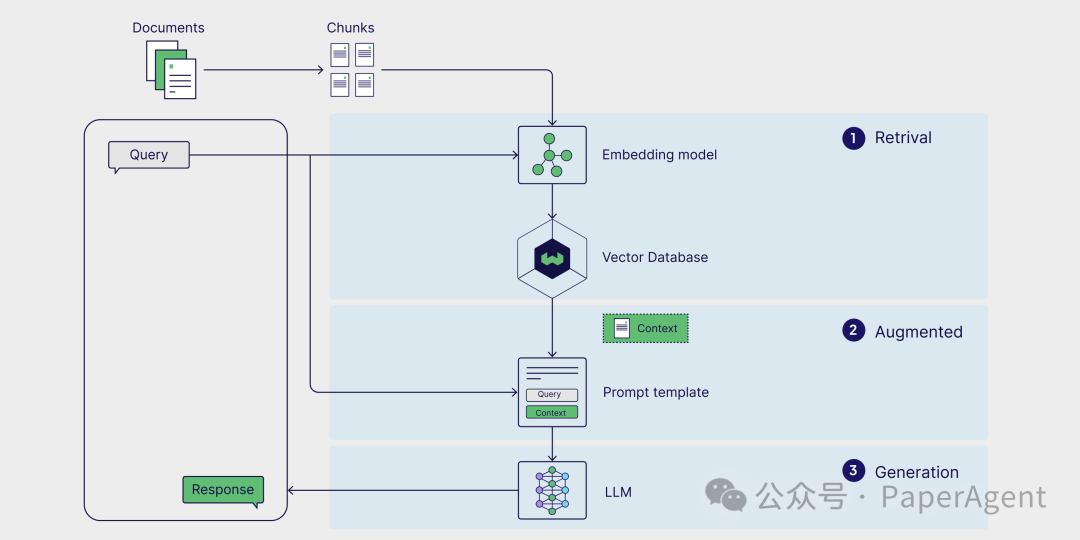
LLM(具有角色和任务) -
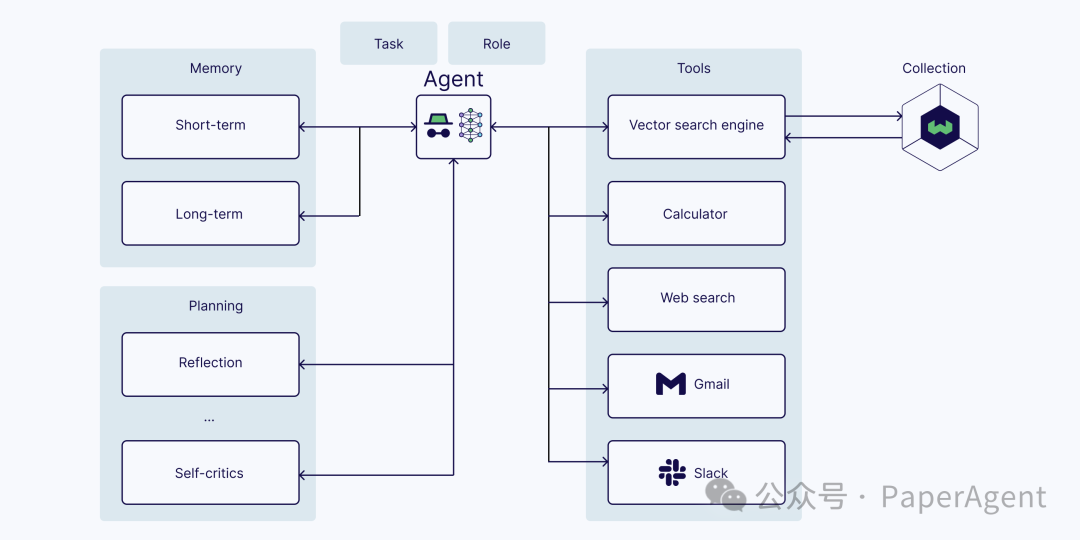
内存(短期和长期) -
规划(例如,反思、自我批评、查询路由等) -
工具(例如,计算器、网络搜索等)
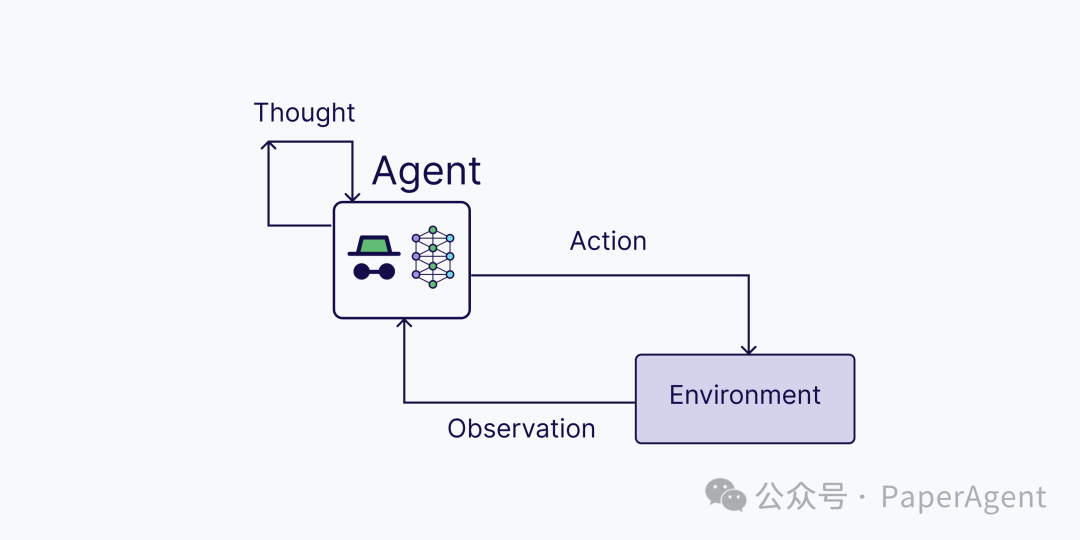
ReAct = 推理 + 行动(使用LLM)
-
思考:在接收到用户查询后,智能体推理下一步行动 -
行动:智能体决定行动并执行它(例如,工具使用) -
观察:智能体观察行动的反馈 -
这个过程一直迭代,直到智能体完成任务并响应用户。
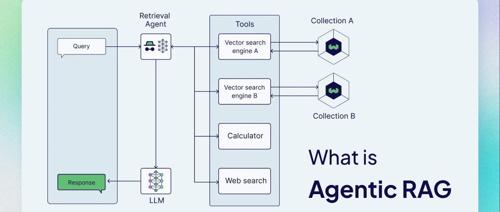
什么是Agentic RAG?
Agentic RAG描述了基于AI智能体实现的RAG。
-
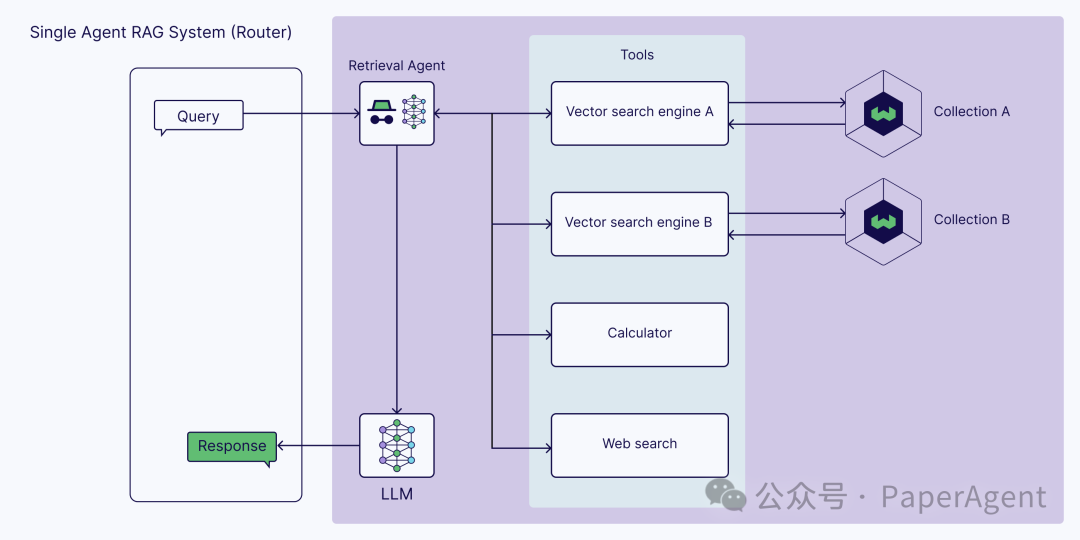
向量搜索引擎(也称为查询引擎),它在向量索引上执行向量搜索(像典型的RAG流程中一样) -
网络搜索 -
计算器 -
任何用于以编程方式访问软件的API,例如电子邮件或聊天程序 -
等等。
-
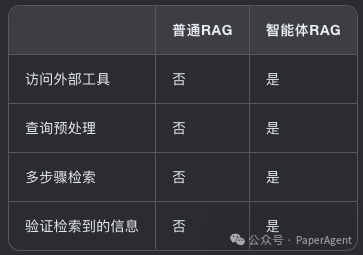
决定是否检索信息 -
决定使用哪个工具检索相关信息 -
制定查询本身 -
评估检索到的上下文,并决定是否需要重新检索。
-
单智能体RAG(路由器)
-
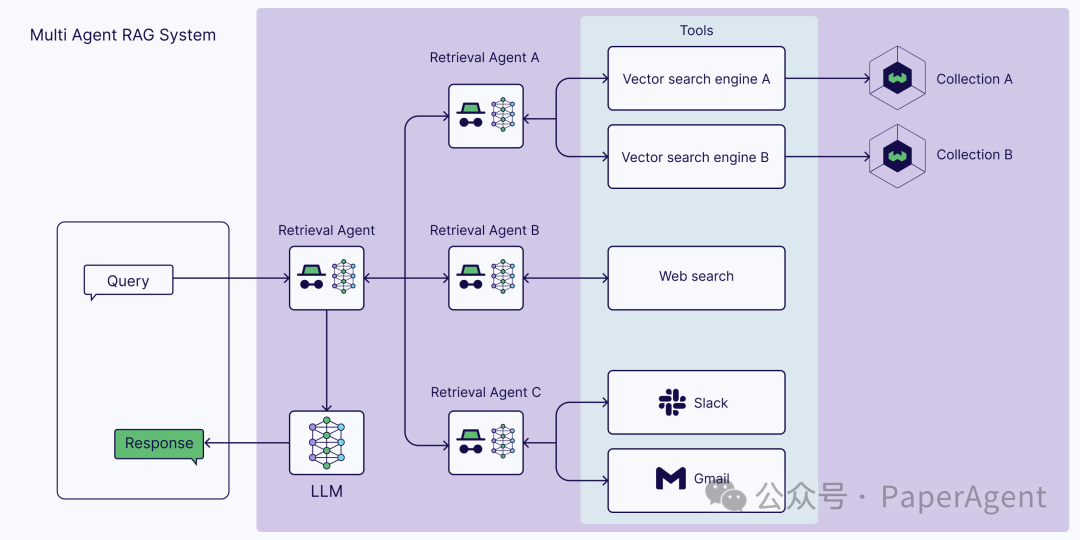
多智能体RAG系统
-
超越检索智能体
Agentic RAG与(普通)RAG
实施智能体RAG
def get_search_results(query: str) -> str:"""Sends a query to Weaviate's Hybrid Search. Parses the response into a {k}:{v} string."""response = blogs.query.hybrid(query, limit=5)stringified_response = ""for idx, o in enumerate(response.objects):stringified_response += f"Search Result: {idx+1}:\n"for prop in o.properties:stringified_response += f"{prop}:{o.properties[prop]}"stringified_response += "\n"return stringified_response
然后我们将函数通过`tools_schema`传递给语言模型。该模式然后在提示中用于语言模型:
tools_schema=[{'type': 'function','function': {'name': 'get_search_results','description': 'Get search results for a provided query.','parameters': {'type': 'object','properties': {'query': {'type': 'string','description': 'The search query.',},},'required': ['query'],},},}]
由于你直接连接到语言模型API,你需要编写一个循环,该循环在语言模型和工具之间进行路由:
def ollama_generation_with_tools(user_message: str,tools_schema: List, tool_mapping: Dict,model_name: str = "llama3.1") -> str:messages=[{"role": "user","content": user_message}]response = ollama.chat(model=model_name,messages=messages,tools=tools_schema)if not response["message"].get("tool_calls"):return response["message"]["content"]else:for tool in response["message"]["tool_calls"]:function_to_call = tool_mapping[tool["function"]["name"]]print(f"Calling function {function_to_call}...")function_response = function_to_call(tool["function"]["arguments"]["query"])messages.append({"role": "tool","content": function_response,})final_response = ollama.chat(model=model_name, messages=messages)return final_response["message"]["content"]
ollama_generation_with_tools("How is HNSW different from DiskANN?",tools_schema=tools_schema, tool_mapping=tool_mapping)
智能体框架
-
DSPy支持ReAct智能体和Avatar优化。Avatar优化描述了使用自动化提示工程来描述每个工具的使用。
-
LangChain为使用工具提供许多服务。LangChain的LCEL和LangGraph框架进一步提供了内置工具。
-
LlamaIndex进一步引入了QueryEngineTool,这是一个用于检索工具的模板集合。
-
CrewAI是开发多智能体系统的领先框架之一。用于工具使用的一个关键概念是智能体之间共享工具。
-
Swarm是由OpenAI构建的多智能体协调框架。Swarm同样专注于智能体之间如何共享工具。
-
Letta将反映和提炼内部世界模型作为函数。这意味着可能使用搜索结果来更新聊天机器人用户的智能体内存,除了回答问题。
https://weaviate.io/blog/what-is-agentic-rag推荐阅读
-
• 对齐LLM偏好的直接偏好优化方法:DPO、IPO、KTO
-
• 2024:ToB、Agent、多模态
-
• RAG全景图:从RAG启蒙到高级RAG之36技,再到终章Agentic RAG!
-
• Agent到多模态Agent再到多模态Multi-Agents系统的发展与案例讲解(1.2万字,20+文献,27张图)
欢迎关注我的公众号“PaperAgent”,每天一篇大模型(LLM)文章来锻炼我们的思维,简单的例子,不简单的方法,提升自己。
(文:PaperAgent)